Overview of creating your own website with WordPress – from installing a theme to creating your own posts
- As soon as you have decided on a domain and the installation and registration have been successfully completed, you should start by taking a look at the settings.
- A theme is then selected which determines the web design to match your content.
- The first pages of the website or blog are then created and finally implemented in the menu structure.
- If you also wish to create posts for the website, categories are added to the menu.
- You should then familiarize yourself with the widgets and have installed the necessary plugins.
- In the backend behind the logo of the CMS WordPress there are some links (e.g. wordpress.org/ wordpress.com) which are very helpful in case of problems or questions.
The first step to creating your own website: Install WordPress
To begin with, you should have received all the important information, such as the name and password of the database, and have decided on a domain and a provider. A domain is the address under which the website can be accessed. There are a few points to bear in mind when choosing a domain. The URL should never be too long, nor should it contain a protected brand name. A .de domain should be chosen for German-language websites. The domain is registered via WordPress by clicking on “Connect domain”. You can also check whether the desired domain is still available.
You can now start the installation. After installation, all WordPress functions can be used immediately. There are basically 2 options available for installation:
- Click installation: Some hosters offer the option of installing WordPress with just a few clicks. This procedure is very simple and fairly quick. Even if this method sounds easy at first, problems may arise later due to the automatic installation.
- Manual installation: As the name suggests, the manual method is more time-consuming and complex, but also better in the long term. However, good basic knowledge of server technology is required for manual installation. The installer should not be afraid of working with databases and FTP access is also a prerequisite.
It should take about 30 minutes to install WordPress yourself. The most important steps are listed here:
- First, an SSL certificate must be set up.
- WordPress is then downloaded and unpacked.
- A database is then created.
- Then set up a wp-config.php file in which you enter the access data for the database.
- The WordPress files are uploaded to the web space, e.g. with an FTP program.
- To carry out the installation, go to “www.beispielwebsite.com/wp-admin/install.php”. “examplewebsite.com” must of course be replaced by your own domain.
- Then follow the steps in the installation instructions.
Login to the admin area of WordPress
You can log in via the WP login page using the access data you specified during installation. The WP login page is the URL of your own website, to which you add “/wp-login.php” in the address bar of the browser. This could be, for example look like this: “www.beispielwebsite.com/wp-admin/install.php”. You will then be automatically redirected to the WordPress admin area.
Choose WordPress hosting
Due to the enormous number of hosting providers, it is not easy to find the right one. WordPress recommends the following system requirements that the host should fulfill:
- MySQL 5.6 or higher / MariaDB 10.1 or higher
- PHP 7.3 or higher
- HTTPS support
- Nginx or Apache with “mod_rewrite module”
- SSD memory
It is best to contact support to find out whether the requirements are met.
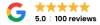
Tutorial on the WordPress dashboard
The dashboard provides a clear overview of all functions. Any area can be accessed and edited via the dashboard, e.g. the design of the website, individual posts or general settings. Each menu item contains several sub-items. When you start working with WordPress, you should get an overview of the options WordPress offers you. To create the basic structure of your website, tutorials on the most important areas in the dashboard follow.
Tutorial Dashboard WordPress
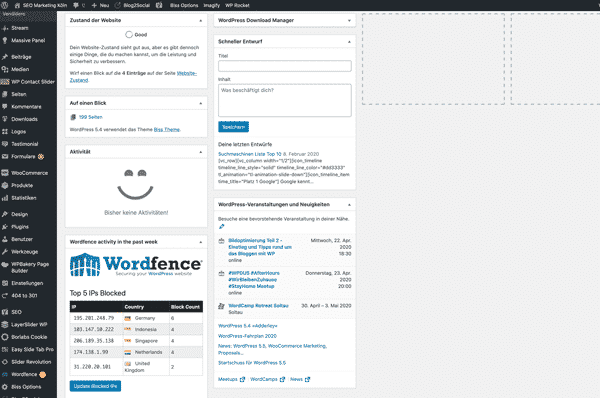
Checking the settings
The settings are checked at the beginning of the WordPress tutorial. In addition to the general settings, such as the language setting, media, comments, posts, etc. can also be configured. You can specify whether website visitors have to log in to post a comment and what permissions they have without logging in. To begin with, all these points should at least be skimmed over before creating your own website or blog.
Tutorial WordPress settings
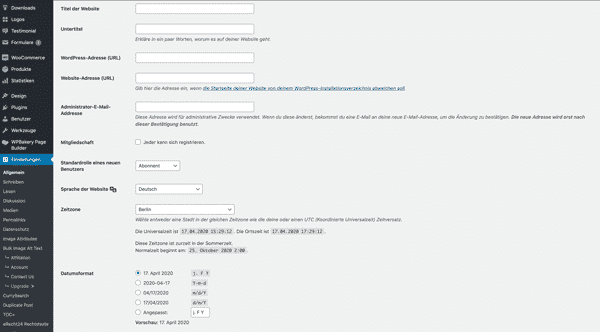
Selecting the themes for the design of the website/blog
The design of the website is determined by the themes. Under the menu item “Design” -> “Themes” you will be offered a large selection of WordPress themes from which you can choose and install the selected theme.
Since the appearance of the website and the content are separate from each other, it is always possible to change them at a later date. In the event of a change, the content of the website remains unchanged and is inserted into the new layout. There are many other options for further customizing the design of the website. For now, however, it is sufficient to select the theme for your website that you like best and that matches the content of your website.
Once you have found a theme, click on “Activate”. You can then view the theme, in combination with your content, and change it again if you wish.
Choose a theme for WordPress
Finding the perfect theme – inspiration for a new design
In most cases, you won’t find a suitable theme straight away and don’t yet have an exact idea of what your website should look like. After all, it is important that the content is reflected in the web design. Even if you can always change the theme later, it’s nicer to be happy straight away and not have to keep changing things. Especially because there are much more important things in WordPress that you should deal with.
So before you select a theme and activate it, it is advisable to look for some inspiration. There are tons of them on the Internet to help you make your choice. It is important that no websites are copied 1:1. It’s just a rough direction. Usually this will also give you new ideas about what you might want to include on your website. The following sources serve as good web design inspiration:
- Webdesign-Inspiration.com – This website offers you a large collection of many different designs, including links and voting functions. It is always advisable to get the opinions of other users about the design.
- ThemeForest.net – This website is ideal for exploring new themes and trends.
- Blogs and forums – If you would like to hear other opinions or experiences, it is a good idea to browse through various online forums or blogs.
Creating pages and posts
Your website consists largely of the pages and Contributions. Pages are used for information that the visitor can access at any time, for example the imprint, directions, data protection, contact, etc.. Posts, on the other hand, are automatically displayed in chronological order. They can be sorted into categories. This can be a single category or several categories. Basically, the creation of the Contributions and pages on a WordPress homepage the same. An editor is available that you can use for both types of content. The editor is based on blocks, with blocks for headings, tables, paragraphs and images. To select or insert a block, click on the “+” symbol at the top left.
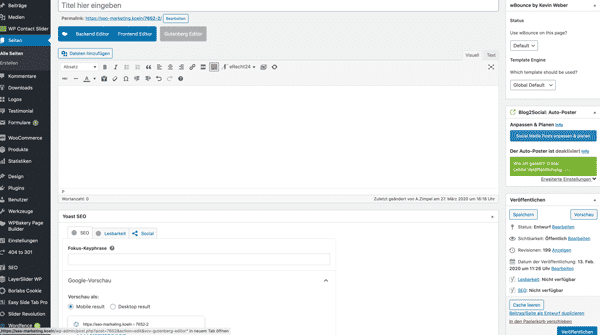
Creating a page on WordPress
Create the navigation on your website
Under “Design” -> “Menus” you have the option of giving your pages a hierarchical structure and integrating it into the menu of your website. The individual elements are arranged using drag-and-drop, and the sub-items are also taken into account. Pages are mainly used for a company’s Internet presence. This is called a static website. In contrast to static websites, blogs consist mainly of articles. If this is the case, it is recommended to add categories to the menu structure.
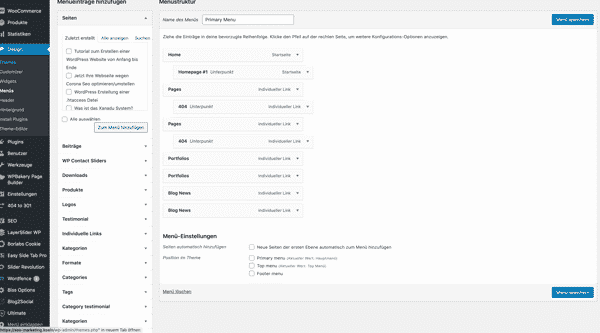
Creating a menu structure in WordPress
Installing plugins in WordPress
WordPress can be extended with a number of useful functions using plugins. WordPress plugins are additional modules for WordPress, so to speak. These can be buttons that are added to the editor, a contact form that is inserted into the website or backup help, for example. Plugins bring many new features that would not be possible with WordPress alone. There are plugins for image galleries, entry forms, newsletters and search engine optimization. The extensive archive of WP plugins can be found under “Plugins” -> “Install”. Some of the plugins can be installed free of charge, while others are subject to a charge. It is very important that plugins are only installed by certified developers, as poorly programmed plugins can lead to security vulnerabilities. Too many plugins can also have a negative impact on performance.

Installing plugins in the dashboard
How is a plugin installed?
As with the themes, installing plugins is very easy. To do this, click on “Plugins” -> “Install”. Then enter the name of the plugin under “Search plugins”. Then click on the installation button and the plugin will be downloaded and installed. Now just click on “Activate” and the plugin can be used.
Select useful widgets
Widgets are small content blocks and can be inserted in the header, sidebar or footer. Normally, a widget only performs a single function and integrates a search function, for example, or displays a preview of the latest posts on the website. Whether a widget should appear on every subpage in the sidebar or only on selected pages can be defined using the widget logic.
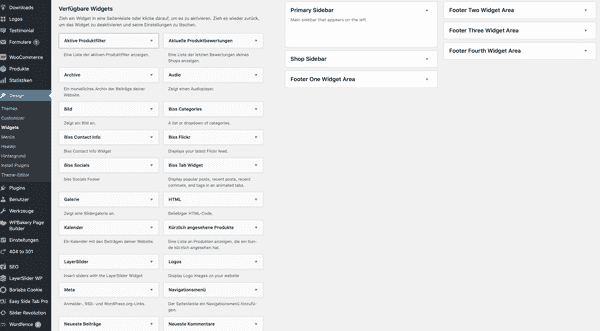
Installing widgets in the theme
Further tips and tricks for better handling of WordPress
Especially at the beginning, while working with WordPress, new questions keep coming up. A quick help is usually provided by a short Internet search. However, the solution could often be found in WordPress itself, namely in the WP backend, where important and, above all, helpful links are stored. To do this, simply move the mouse over the WordPress logo:
Recommendations from WordPress
- We also recommend the main page of WordPress(wordpress.org) where you can find the latest WordPress versions and many helpful articles.
- Support forums are a great way to get in touch with other WordPress users who may have had the same questions and have already found a solution. For example Questions about the editor, dashboard, settings or installation, themes, widgets and plugins can be answered or the difference between posts and pages can be clarified.
- For complex questions that are particularly technical, English-language forums are a good option as the community is larger.
- The link codex.wordpress.org is particularly recommended for those who deal with the detailed editing and customization of WordPress. You will also learn how to create child themes, for example. There are also installation instructions and explanations of the most important functions.
Tutorial after creating your own homepage
Once you have familiarized yourself with the functions of WordPress and the basic structure of your website is ready, there are still a few things you should take care of. The following topics should be considered when continuing to use WordPress:
Installation of a security plugin
Right from the start, you should pay attention to the protection of your Internet presence and ensure adequate security measures. This starts with choosing a secure password. Plugins help to protect your website, as there are several extensions that offer functions such as the restriction of login attempts before access is blocked. By simply trying out the password, hackers now have virtually no chance of guessing the correct password. The installation of a security plugin is particularly worthwhile for comprehensive protection, as it directly fulfills several functions. One such security plugin is “Wordfence Security”, for example.
Avoiding the causes of a slow website
Even if plugins are very helpful and can extend WordPress with some functions, too many installed plugins can lead to an overloaded website. As a result, the website takes a long time to load, which means that readers leave the website again. You should therefore find out right at the start what can influence a long loading time in order to avoid this. A slow website often occurs due to the following causes:
- Particularly elaborate themes with many effects
- poor code quality
- Image files too large
- Too many activated plugins
Search engine optimization
For your website to have any chance at all of being found by interested readers, it is important that it has a good ranking. So don’t put off the topic of search engine optimization for too long and find out about your options. You can also get help via the plugins, e.g. one of the most popular and comprehensive SEO plugins, Yoast SEO. This plugin provides additional SEO functions and gives many tips.
Common errors when using WordPress
The CMS (Content Management System) WordPress has always been considered very user-friendly due to its simplicity and usability. It is now the most popular CMS and millions of websites are based on it. WordPress is particularly suitable for beginners, as it requires no prior knowledge and you can fill a blog or website within a few minutes.
Unfortunately, user-friendliness has meant that small errors can quickly appear. These errors have a detrimental effect on the security of the website or search engine optimization. The following errors occur frequently and should therefore be avoided:
- Tags are used incorrectly – tags are subject areas that could also be called categories. If too many of these are used or the tags are used incorrectly, they will be indexed by Google and therefore have a negative effect on search engine optimization.
- Too many installed plugins – Plugins are supposed to extend WordPress with some functions. However, if too many of these are installed, especially unnecessary plug-ins, the security and performance of the website will suffer.
- Neglecting backups – Backups should always be made regularly so that no data can be lost and the security of the website is therefore guaranteed.
What is the difference between wordpress.com and wordpress.org?
WordPress.org is a free open source software for websites, blogs and apps for download, which also offers plugins and themes. However, the software must be installed by your own hoster. This means that a paid web space is required on which the WP website can be hosted.
WordPress.com is a member area where you can register free of charge and which offers several features as a complete package. This includes the hosting as well as the CMS (Content Management System) and a domain. This package can be purchased free of charge with the Free plan, but does not include your own domain. This means that at the end of the domain “
WordPress.com is very limited in terms of extensions. WordPress.org, on the other hand, offers more freedom, but the CMS must be installed on your own server or web space.
The decision between .com or .org depends on the purpose of the website. So if the website is to be created completely free of charge, the free plan from wordpress.com must be used. However, if the website is more extensive, such as company websites, online stores or large blogs, wordpress.org offers significantly more advantages.
Tutorial for editing the WordPress codes
The WordPress codes can be edited to gain more control over how the website or blog looks and functions. Various areas can be customized:
- Subordinate themes can be used to edit the source code of WordPress themes.
- There are two ways to add a user-defined CSS (Cascading Style Sheet). You can use a plugin such as Simple CSS or add CSS in the WordPress Customizer via the “Additional” section.
- The HTML code can be edited for individual pages or posts using the new block editor or the classic editor.
- Plugins can be used to manage code snippets that are added to the or functions.php file of your own theme.
Edit WordPress HTML for individual posts or pages
There are several ways to work with HTML in the Gutenberg Editor, but first a brief explanation of what the Gutenberg Editor actually is.
Since WordPress version 5.0, pages and posts have been edited with a completely new editor, namely the Gutenberg Editor. Compared to the well-known PageBuilders, not much has changed, except that the Gutenberg Editor is much faster and there are fewer blocks, which simplifies the overall design.
This opens up new possibilities for designing your website, as the block-based editor means that many websites no longer need a PageBuilder. Another advantage is that no special prior knowledge or an additional PageBuilder plugin is required.
If you want to add your own HTML code to a part of the content, you should not edit the entire source code of the page. Instead, the custom HTML block can be used and the code inserted.
If you need to edit the HTML code of another block directly, there are two options to choose from. This can happen, for example, if you want to add a nofollow tag to a link in the block editor.
- You can click on the options for a single block and select the “Edit as HTML” option
- To edit the HTML for an entire post, you can access the code editor via the “Tools & Options” drop-down list. This key combination Ctrl + Shift + Alt + M speeds up this process and you can easily switch between visual editing and code.
Add custom CSS (Cascading Style Sheet) to WordPress
If you only want to add the user-defined CSS instead of the HTML code, you do not need to use the integrated code editor. Instead, you can use the WordPress Customizer. This is a simpler option for now and another advantage is that a preview of the changes can be displayed in real time.
- First click on “Appearance” -> “Customize” in the WordPress dashboard.
- After you have accessed the WordPress Customizer, select the “Additional CSS” option.
- A code editor will now open in which you can add the desired CSS. As soon as this has been added, the live preview of the website is automatically adjusted or updated to reflect the changes.
Another option is to use a plugin, e.g. the Simple CSS plugin. This offers similar options to the WordPress Customizer. You can also add custom CSS to individual pages or posts via a meta box.